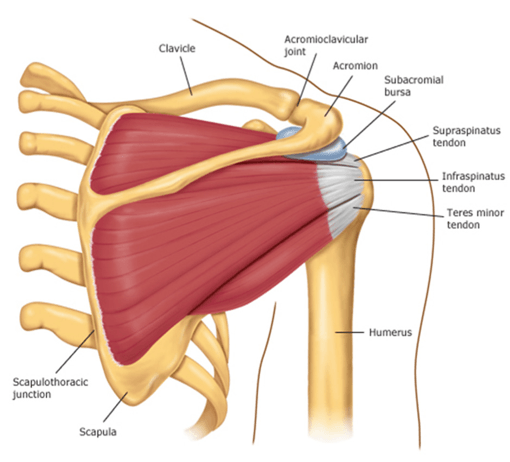
ANATOMY
Your shoulder is made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle).
Your arm is kept in your shoulder socket by your rotator cuff. These muscles and tendons form a covering around the head of your upper arm bone and attach it to your shoulder blade.
There is a lubricating sac called a bursa between the rotator cuff and the bone on top of your shoulder (acromion). The bursa allows the rotator cuff tendons to glide freely when you move your arm.
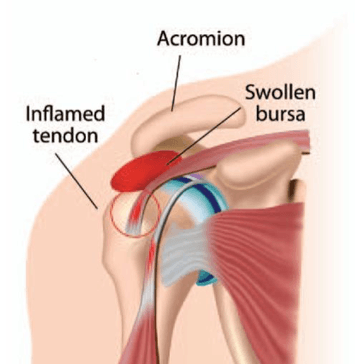
The rotator cuff is a common source of pain in the shoulder. Pain can be the result of:
- Tendinitis.The rotator cuff tendons can be irritated or damaged.
- Bursitis.The bursa can become inflamed and swell with more fluid causing pain.
- Impingement.When you raise your arm to shoulder height, the space between the acromion and rotator cuff narrows. The acromion can rub against (or “impinge” on) the tendon and the bursa, causing irritation and pain.
CAUSES
Structural Narrowing, Conditions such as osteoarthritis can cause the growth of sub-acromial bony spurs, which further narrows the space you are more likely to squash, impinge and irritate the soft tissues in the sub-acromial space,
Dynamically Unstable- Excessive joint movement, ligament laxity and muscular weakness around the shoulder joint. It usually occurs over time due to repetitive overhead activity, trauma, previous injury, poor posture or inactivity.
Rotator cuff weakness- When your rotator cuff fails to work normally, it is unable to prevent the head of the humerus (upper arm) from riding up into the sub-acromial space, causing the bursa or tendons to be squashed.
SYMPTOMS
Beginning symptoms may be mild. These symptoms may include:
- Minor pain that is present both with activity and at rest
- Pain radiating from the front of the shoulder to the side of the arm
- Sudden pain with lifting and reaching movements
- Athletes in overhead sports may have pain when throwing or serving a tennis ball
As the problem progresses, the symptoms increase:
- Pain at night
- Loss of strength and motion
- Difficulty doing activities that place the arm behind the back, such as buttoning or zippering
TREATMENTS
In most cases, initial treatment is nonsurgical. Although nonsurgical treatment may take several weeks to months, many patients experience a gradual improvement and return to function.
Rest. Your doctor may suggest rest and activity modification, such as avoiding overhead activities.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines. Drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen reduce pain and swelling.
Physical therapy. A physical therapist will initially focus on restoring normal motion to your shoulder. Stretching exercises to improve range of motion are very helpful. If you have difficulty reaching behind your back, you may have developed tightness of the posterior capsule of the shoulder (capsule refers to the inner lining of the shoulder and posterior refers to the back of the shoulder). Specific stretching of the posterior capsule can be very effective in relieving pain in the shoulder. Once your pain is improving, your therapist can start you on a strengthening program for the rotator cuff muscles.
Steroid injection. If rest, medications, and physical therapy do not relieve your pain, an injection of a local anesthetic and a cortisone preparation may be helpful. Cortisone is a very effective anti-inflammatory medicine. Injecting it into the bursa beneath the acromion can relieve pain.
Surgical treatments-. Continued pain is the main indication for surgery. If you are very active and use your arms for overhead work or sports, your doctor may also suggest surgery.
Other signs that surgery may be a good option for you include:
- Your symptoms have lasted 6 to 12 months
- You have significant weakness and loss of function in your shoulder
- Your tear was caused by a recent, acute injury





